The optimal seat-to-back angle does more than just improve comfort — it enhances overall wheelchair performance. By providing the right balance between stability and mobility, it helps users maintain a natural upright posture, reduces long-term sitting discomfort and pressure, and supports users sit upright effortlessly, avoid slouching, and enjoy a wider field of vision.
A well-adjusted seat angle also promotes better breathing and digestion, while making transfers easier and safer for caregivers. For wheelchair users who spend extended hours seated, this ergonomic design elevates both body performance and social confidence, delivering a smoother, healthier, and more active wheelchair experience.
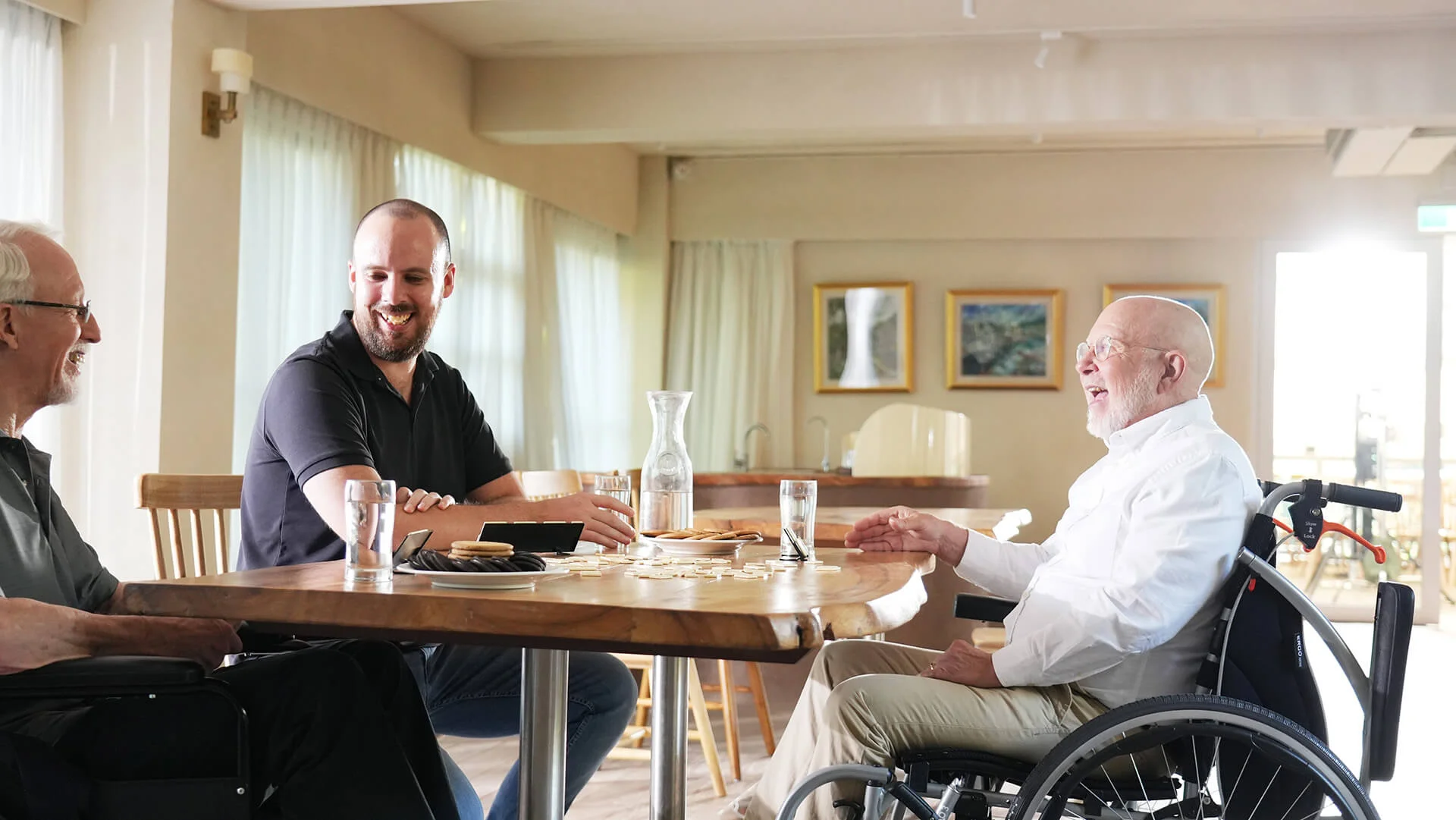

What Is the “Golden Seat-to-Back Angle” for wheelchairs?
The so-called “golden seat-to-back angle“ is made up of two key components that work together to create the ideal sitting posture for wheelchair users.
Key Angle 1: The Wheelchair Seat Angle
The seat angle determines how stable the user’s sitting posture is in the wheelchair.
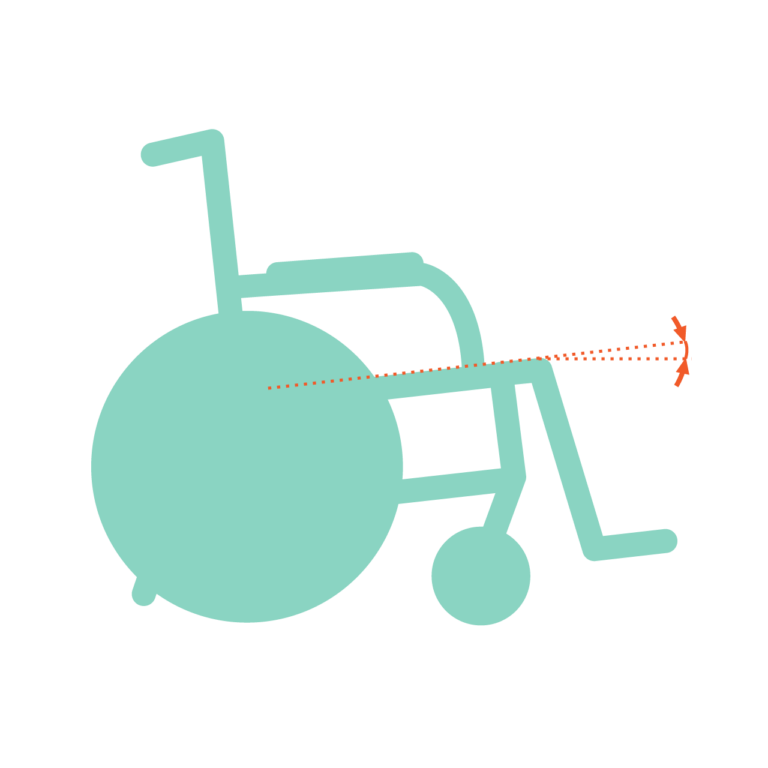
The seat angle affects pelvic tilt and stability — and a stable pelvis means a stable sitting posture.
- Flat seat (0°): The user must rely entirely on their own strength to stay upright. When muscle strength is limited, the pelvis tends to tilt backward, leading to slouching or sliding forward in the seat.
- Negative seat angle (front lower than back): The body naturally leans forward, making users easier to stand up. However, after about 30 minutes, the user may unconsciously lean backward to stabilize the posture, concentrating pressure on the sitting bones and increasing the risk of pressure sores.
- Positive seat angle (the front slightly higher, around 3°–7°): This helps the body lean naturally against the backrest, improving pelvic stability and reducing forward sliding. It also promotes a more relaxed, balanced, and comfortable sitting position.
In short, the pelvis is the foundation of posture. Once it tilts or slides, the upper body loses stability, causing fatigue and discomfort. The right seat angle “locks in“ the pelvis, allowing the back to rest securely and the user to move more efficiently with less effort.
Key Angle 2: The Seat-to-Backrest Angle

The seat-to-backrest angle plays a crucial role in overall sitting comfort and stability.
- The seat-to-backrest angle determines how stable the upper body remains while seated.
- Smaller angles (less than 90°–95°): These help stabilize the pelvis and improve upper-body mobility. However, when maintained for long periods, they may cause the pelvis to tilt backward, leading to slouching, spinal strain, and restricted chest expansion.
- Moderate angles (between 95°–110°): Opening the angle slightly relieves pressure on the waist and abdomen, allowing for easier breathing and greater comfort. It also helps users with limited hip flexibility maintain a more stable, supported position.
- Larger angles (over 110°): A more reclined position can reduce sitting pressure and enhance relaxation during extended use. Still, it‘s important to watch for forward pelvic sliding and reduced mobility when reclining too far.
For users with good physical function, the ideal seat-to-backrest angle is typically between 95° and 105°, offering the best balance between stable support and long-term comfort.
The golden angle to maintain eyesight
α = the seat-to-backrest angle; φ = the seat angle;
α+φ = Functional Angle
Adjusting only the backrest angle isn‘t enough to stabilize the pelvis. Without a proper seat angle, the pelvis can still slide forward. The true “golden“ seat-to-back angle requires the right combination of both angles to create a stable pelvic foundation. This allows users to sit upright effortlessly, lift their heads naturally, and enjoy a clearer view as well as a fuller life.
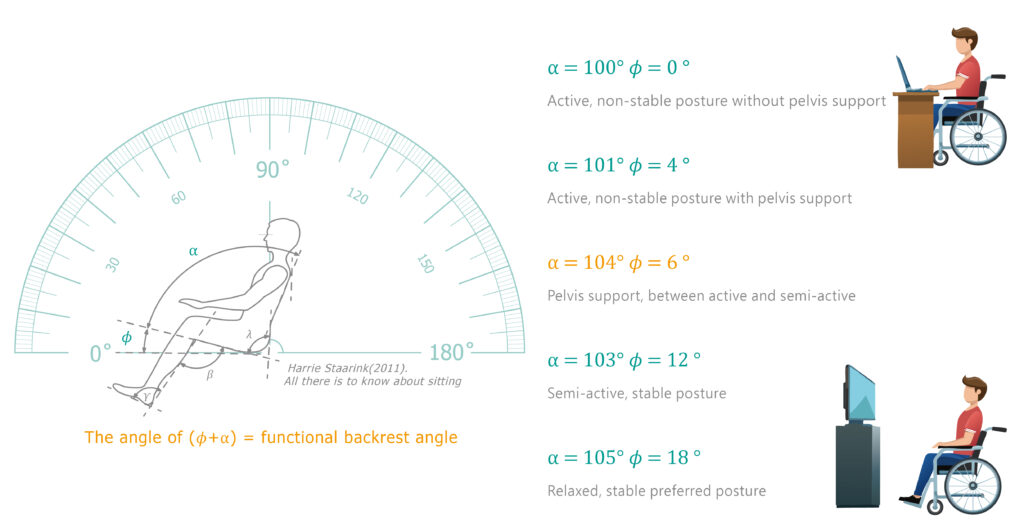
The Impact of the ⍺ + 𝜙 Functional Angle on Wheelchair Users《All there is to know about sitting》(Harrie Staarink. 2011)
The 4 Benefits of the Golden Seat-to-Back Angle
- Improves Posture and Spinal Health
A gentle recline helps distribute spinal pressure evenly, reducing the risk of scoliosis or hunching caused by long hours of sitting upright or leaning forward. - Relieves Discomfort and Increases Sitting Endurance
By stabilizing the pelvis, the golden seat-to-back angle reduces the risk of pressure injuries and enhances comfort for prolonged sitting. - Opens the Chest and Boosts Breathing Efficiency
A slightly reclined posture expands the chest cavity, allowing smoother, deeper breathing. For users who spend long hours in a wheelchair, this means less fatigue and more energy throughout the day. - Builds Confidence and Encourages Social Engagement
When users can sit upright and meet others at eye level, conversations flow more naturally.
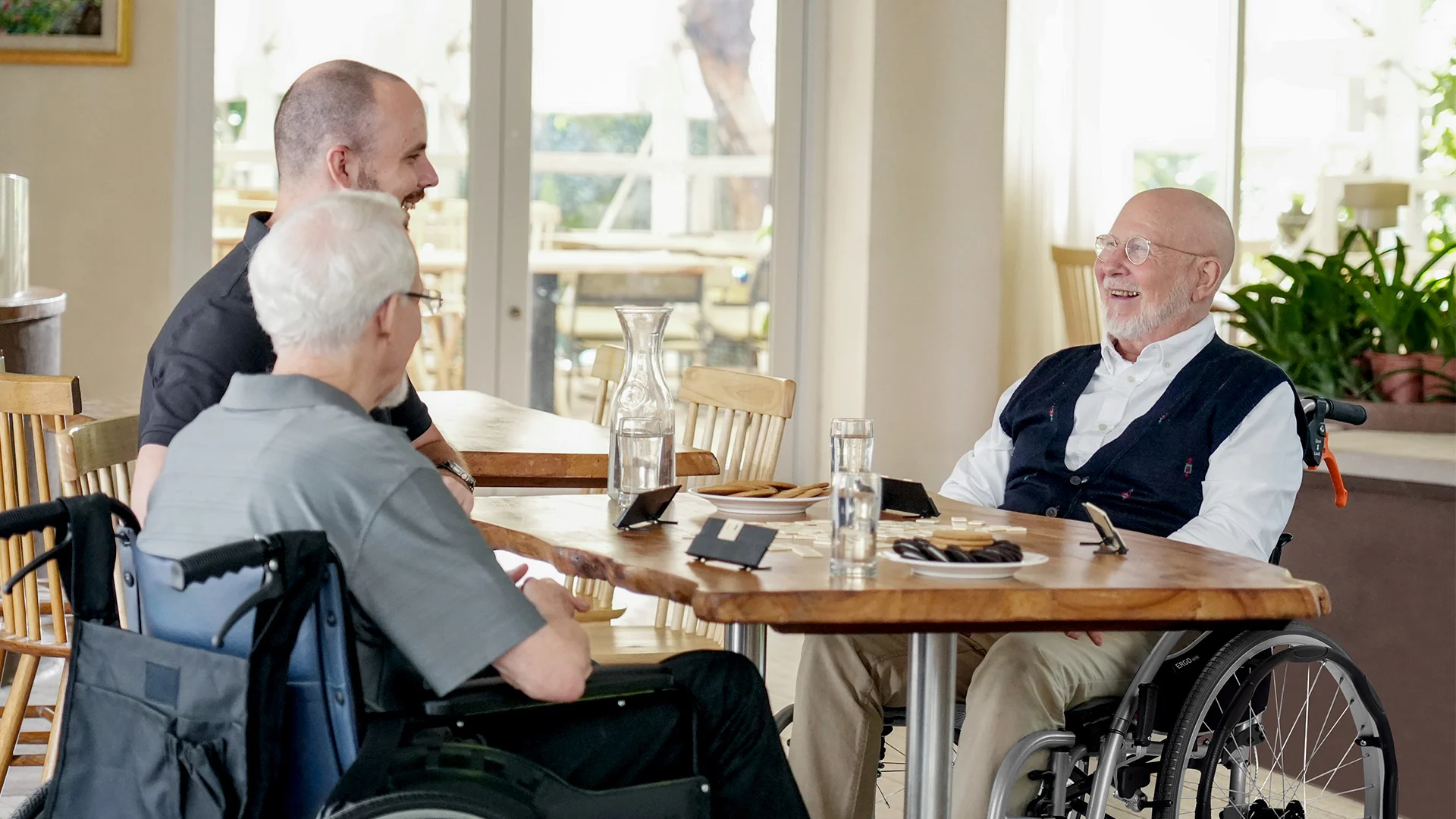

Therapists have observed that after adjusting to the ideal angle, users become more willing to engage in community events — because lifting your head is, in itself, an expression of confidence.
How to Find Your Golden Angle
- Professional Evaluation: Start with a posture assessment by a seating specialist or therapist.
- Dynamic Adjustment: Different activities such as reading, relaxing, socializing, may require different angles. Choose a wheelchair with adjustable seating functions for flexibility.
- Comfort First: There‘s no universal “perfect“ angle. The best setup is the one that supports your body, relieves pressure, and helps you sit tall comfortably.
More Than Medical — It’s About Everyday Living
An incorrect seating angle can often lead to slouching or downward gazes, causing both discomfort and a lack of confidence. In contrast, when the seat-to-back angle is properly adjusted, users can look up and meet others‘ eyes — a simple yet powerful step toward genuine connection.
The golden seat-to-back angle isn‘t just about comfort; it‘s a clinically supported and ergonomically proven way to achieve the best sitting posture.
Ergo 3, The wheelchair designed around the Golden Seat-to-Back Angle, reduces physical strain, enhances breathing and focus, and helps users engage naturally in social interaction.
From posture and breathing to confidence and connection — Ergo 3 supports your every moment.
👉 Discover Ergo 3 Today
FAQ
Q1: What Is the Golden Seat-to-Back Angle?
A: The Golden Seat-to-Back Angle refers to the Functional Angle, formed by the combination of the seat angle and the seat-to-backrest angle. This ergonomic setup helps stabilize the pelvis, distribute sitting pressure, expand the user‘s field of vision, and boost social confidence. The ideal range is generally around 110°.
Q2: Why Does the Backrest Angle Affect Breathing and Digestion?
A: When the backrest is too upright or the user slouches, the chest and abdomen are compressed, leading to shallow breathing and poor digestion. A slightly reclined position allows the chest to open up, improving oxygen flow, easing abdominal pressure, and enhancing energy levels.
Q3: Can the Golden Seat-to-Back Angle Prevent Pressure Sores?
A: Not completely. The right sitting angle can help stabilize the pelvis and redistribute pressure across the thighs and buttocks, reducing concentration on the sitting bones. However, preventing pressure sores still requires additional strategies, such as using an air cushion and performing regular pressure-relief movements.
Q4: Is There One Universal Golden Angle for Everyone?
A: No. The Golden Angle serves as a guideline rather than a fixed standard. Since every user‘s body and mobility needs are different, the ideal angle should be determined through a professional seating assessment by a therapist or assistive device center.
Q5: What Makes Ergo 3 Special?
A: Ergo 3 is the wheelchair designed around the Golden Seat-to-Back Angle. It balances pelvic stability, smooth breathing, and confident posture, helping users achieve true harmony between health and everyday living.
Keep Reading

 Global
Global

